CNC Machine G Codes
2024-08-21 14:17:41
The G-code on CNC equipment is the instruction set used by the device, and the microcontroller can read and execute these commands to control the motion of the CNC device, such as CNC lathes or milling machines. This article explores CNC equipment G-codes in depth, mainly introducing their functions, importance, and applications.
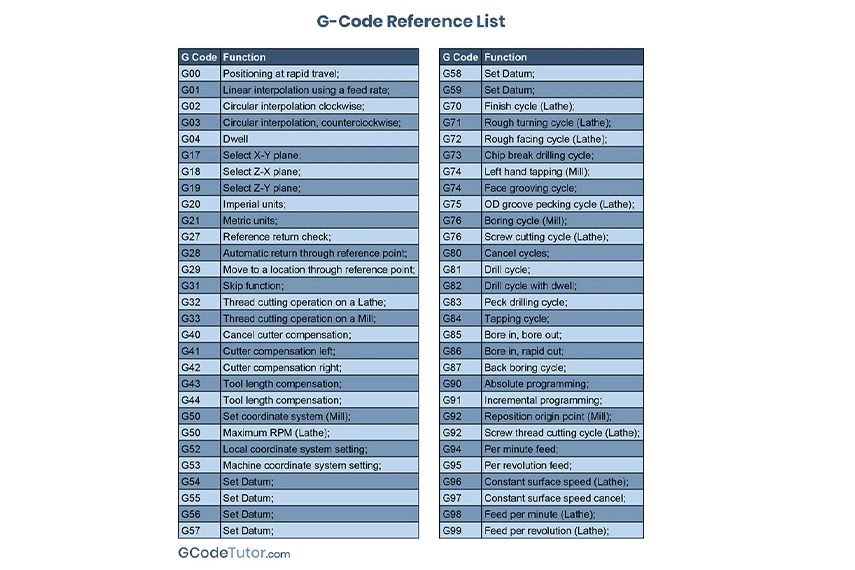
Introduction to G Codes
G codes are a part of the numerical control programming language used to control CNC machines. They are essential commands that guide the machine’s movements and operations, defining parameters such as speed, feed rate, and tool positioning. G Codes dictate the operational characteristics of machine tools, including the type of motion (linear or curved), direction, speed, and feed rate. Each G Code serves a unique function. For instance, G00 and G01 are responsible for rapid positioning and linear interpolation, respectively. In contrast, G02 and G03 control the machine's circular interpolation, both clockwise and counterclockwise. G codes, which stand for "Geometric Codes," form the foundation of CNC programming and are standardized across various CNC systems, although there may be slight variations depending on the machine and controller manufacturer.
Structure of G Codes
A typical G code command consists of a letter (G) followed by a numerical value. This combination instructs the machine on specific actions. For example, the command G01 instructs the machine to move in a straight line at a specified feed rate, while G02 commands a clockwise arc movement. The structure of a G code line often includes additional parameters such as coordinates (X, Y, Z), feed rates (F), and spindle speeds (S). Here’s a breakdown of a typical G code line:
G01 X10 Y20 Z-5 F100
In this example:
- G01: Indicates a linear interpolation move.
- X10 Y20 Z-5: Specifies the end coordinates for the movement.
- F100: Sets the feed rate to 100 units per minute.
The Role of G Codes in Manufacturing
G Codes play a pivotal role in a wide array of manufacturing processes, including milling, drilling, turning, and grinding. They orchestrate the movements of the machine, guaranteeing precision and consistency in the production process. For example, the G81 code is utilized for drilling cycles, while G20 and G21 set the measurement units to inches and millimeters, respectively. More complex operations often require a combination of various G Codes to achieve the desired outcome.
Applications of G Codes in CNC Machining
G codes are used in various CNC machining operations, including milling, turning, and drilling. Each operation requires specific G codes to control the movement and operation of the machine. Here are some common applications:
Milling Operations
In milling operations, G codes control the movement of the cutting tool along multiple axes. Common milling operations include:
- Facing: Creating a flat surface on the workpiece.
- Contour Milling: Following a complex path to shape the workpiece.
- Pocket Milling: Removing material from an interior cavity.
G codes such as G01, G02, and G03 are frequently used in these operations to control linear and circular movements.
Turning Operations
In turning operations, G codes control the movement of the workpiece and the cutting tool on a lathe. Common turning operations include:
- Facing: Creating a flat surface perpendicular to the workpiece's axis.
- Turning: Reducing the diameter of the workpiece.
- Threading: Cutting threads on the workpiece.
G codes like G00, G01, and G28 are often used in turning operations to position the tool and control its movement.
Drilling Operations
In drilling operations, G codes control the movement of the drill bit along the Z-axis to create holes in the workpiece. Common drilling operations include:
- Spot Drilling: Creating a shallow hole to guide the drill bit.
- Peck Drilling: Drilling in stages to reduce heat and improve chip removal.
- Reaming: Enlarging an existing hole to a precise diameter.
G codes such as G81, G82, and G83 are used in drilling cycles to automate these operations.
Conclusion
G-code is an essential and indispensable part of CNC machining projects, providing precise and detailed instructions for machining operations. Understanding various G-codes helps you achieve higher quality machining results.
See What Lunyee Can Do For You
Contact Us
- 8619149417743
- +86-0371-5562 0274
- [email protected]
- Zhengzhou, Henan Province, China
- Mon-Fri: 9:00 - 18:00




